STEM, which stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, is more than just a group of subjects. It’s a way of integrating these crucial areas into a holistic approach to learning and problem-solving.
As I explore STEM, I envision it as a fusion recipe that blends four basic ingredients to prepare students for the jobs of tomorrow. This educational framework aims to develop not only knowledge but also the ability to apply that knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
- STEM intertwines science, tech, engineering, and math for integrated learning.
- A quality STEM education encourages problem-solving and real-world application.
- STEM fields are known for their significant growth and lucrative job opportunities.
Fundamentals of STEM

STEM education is genuinely at the forefront of preparing students for the tech-savvy job market that awaits them, or really, any job they would like to pursue.
Definitions and Components of STEM
STEM, the acronym, rolls off the tongue a bit easier than saying science, technology, engineering, and math each time, right? These four pillars are more pivotal than they have ever been. You see how fast the world changes.
I don’t think I’m that old, but I do remeber my teacher telling me I won’t always have a cacular in my pocket, (jokes on her right!?)
STEM is not just a collection of subjects, but an interdisciplinary approach. That’s really what sets it apart from “just learning.” It’s about interconnecting these fields to solve real-world problems rather than studying them in isolation.
Science explores the natural world, from atoms to ecosystems. Technology is all about gadgets and software – basically anything to make our lives easier and more connected.
Engineering is where design and utility meet, crafting everything from bridges to circuit boards. And let’s not forget math, the language that underlies it all, where we crunch numbers and patterns to predict outcomes. Where we have to prove it on paper to show that the “math works.”
History and Evolution of STEM
Back in the early 2000s, educators coined the term “SMET” but let’s be honest, it wasn’t catchy. Thankfully, Winona State University President Judith Ramaley had a lightbulb moment and switched the letters around to STEM — score one for marketing!
This idea wasn’t just a fresh coat of paint on an old concept; it signified a shift in thinking. Educators recognized the need for students to engage with these subjects cooperatively.
They revamped curricula to reflect this, realizing that the challenges of tomorrow require people who don’t just memorize facts but understand how to apply knowledge creatively and collaboratively. Facts don’t matter; if there is nothing practical, you get out of them.
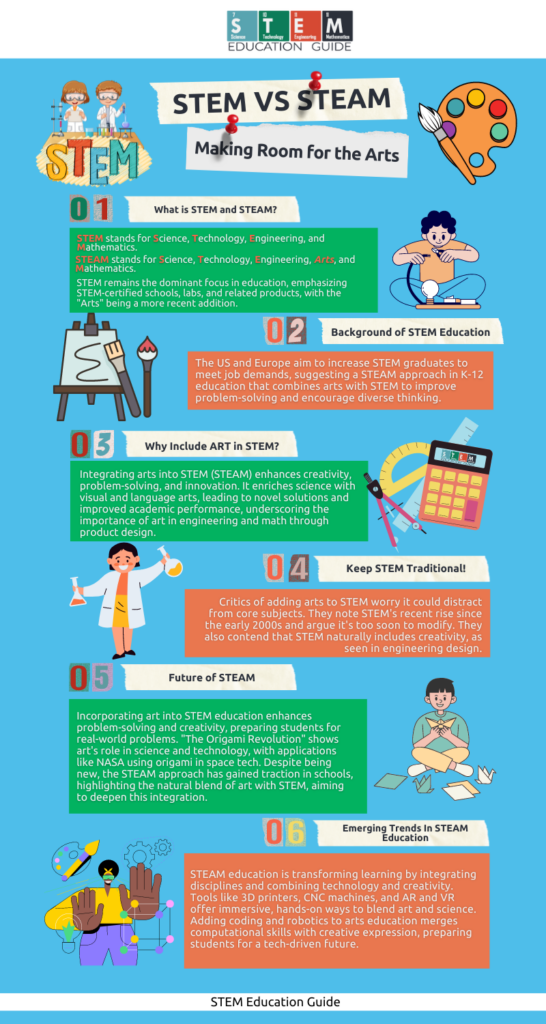
This shift also led to the introduction of STEAM, where the ‘A’ stands for the Arts, acknowledging that creativity is just as crucial in innovation.
If you’d like to read more about STEAM, please take a look at our article: STEM vs. STEAM, Making Room for The Arts.
STEM Education
STEM education isn’t just a bunch of subjects thrown together; it’s about blending science, technology, engineering, and math in a way that gets students ready for a future where these skills will be in high demand.
Let’s get into what makes STEM education so important in schools and how it’s taught beyond the classroom walls.
Importance of STEM in Schools
STEM education is critical for young minds in elementary, middle, and high school. It’s not just about prepping U.S. students for the workforce. It’s about building literacy in STEM fields that sets a foundation for any career path they might choose later on.
I see firsthand how essential STEM skills are for development. When students get a taste of project-based learning, they’re building bridges to the future.
Curriculum and Learning Models

At its best, it incorporates a variety of learning models.
Blended learning is an excellent example, where students spin their gears online and hands-on. Doing research online or on the computer is fine, but students need to get away from the screen and get their hands on something to understand it fully.
Special shout-out to the interdisciplinary nature of STEM that bonds different subjects coherently.
Imagine it: A high school programming task suddenly throws in a curveball from physics, sparking a lightbulb moment for a student. It’s all about making connections, much like piecing together a puzzle that reveals a bigger picture.
STEM Beyond the Classroom

The magic of STEM doesn’t vanish when the school bell rings and the kids leave.
STEM literacy is an ongoing journey that extends to after-school programs, coding boot camps, and DIY science kits at home. High school students often roll up their sleeves in science fairs or internships that provide hands-on experience with real-world applications.
Seeing K-12 students approach everyday problems with a STEM mindset proves how valuable these skills are outside the traditional learning environment.
It’s a testament to the adaptability and relevance of STEM education that it doesn’t restrict itself to classroom corners.
It spills out, influencing how young minds perceive and interact with the world around them.
Understanding the basics of stem is just the beginning. Let’s go a little deeper and read our article on ‘How can STEM education shape the future’ and discover its pivotal role in molding tomorrow’s leaders.
Key Areas of Focus in STEM
Let’s get into the core components of STEM.
Science and Mathematics
Science is where curiosity meets experimentation. From physics to biology and chemistry, science encompasses various disciplines that allow us to understand the natural world.
Think of biology as studying life, chemistry as exploring substances, and physics as the foundation of natural phenomena.
It’s the blend of these natural sciences that provides us the canvas to paint our understanding of life, matter, and the forces that bind them.
Then there’s mathematics. The language of logic, it runs through the veins of STEM like a binding melody.
From basic algebra and geometry to brain-bending calculus and statistics, math provides tools for solving problems big and small.
Whether you find yourself calculating the area of complex shapes or crunching big data through statistical analysis, mathematics is the trusty sidekick to the sciences, making sense of patterns and quantifying our discoveries.
Technology and Engineering
Now, for technology and engineering – they’re the builders of our modern world that we always see.
Both fields rely on applying what we learn from science and math to create tangible solutions. Engineering is the practical application of those disciplines to design everything from bridges and gadgets to the device you’re using right now, with subdivisions like electronics and robotics.
Speaking of gadgets, Technology is the umbrella under which those gadgets dance in the rain of progress.
It includes information systems like computer science, which basically allows us to chat, share, and store information instantly.
Engineering and tech are the forces driving us forward, and they’re constantly evolving, so staying on top of the latest developments is as exciting as essential.
With each area interlacing closely with the others, STEM creates an intricate dance of knowledge that pushes the boundaries of what we can achieve.
It’s not just about individual brilliance, like that of mathematicians or scientists, but about collective progress in these interdependent fields.
Career Perspectives in STEM

In STEM fields, the job landscape is vibrant, with plenty of room for newcomers like me to hop in.
Job Market and Demand
Isn’t it something? Data points to a 79% employment growth in STEM fields over three decades. What’s more, they peg an 11% boom from 2020 to 2030.
It’s not just IT and computer science; areas like electrical and mechanical engineering are also on fire.
As a STEM enthusiast, I can barely contain my excitement over these spirited demands in the job market.
| Field | Expected Growth |
|---|---|
| IT | High |
| Computer Science | High |
| Engineering | Moderate to High |
| Mathematics | Moderate |
STEM Professions and Skills
I’ve seen how STEM majors queue up to get into roles that require not just technical prowess but also an analytical mindset and the agility to navigate an economy fueled by continuous research and development.
The National Science Foundation says we STEM professionals are the backbone of innovation and economic growth, and who am I to argue?
High salary prospects sweeten the deal, especially in roles like systems managers where numbers can bubble up to six figures.
Here’s what’s trending in skills and roles:
- Computer Science & IT: Coding, cybersecurity, and data analytics are gold.
- Engineering: Both electrical and mechanical engineering demand creative problem-solving.
- Mathematics: Skills in analysis and modeling can weave through various sectors.
Broadening Participation
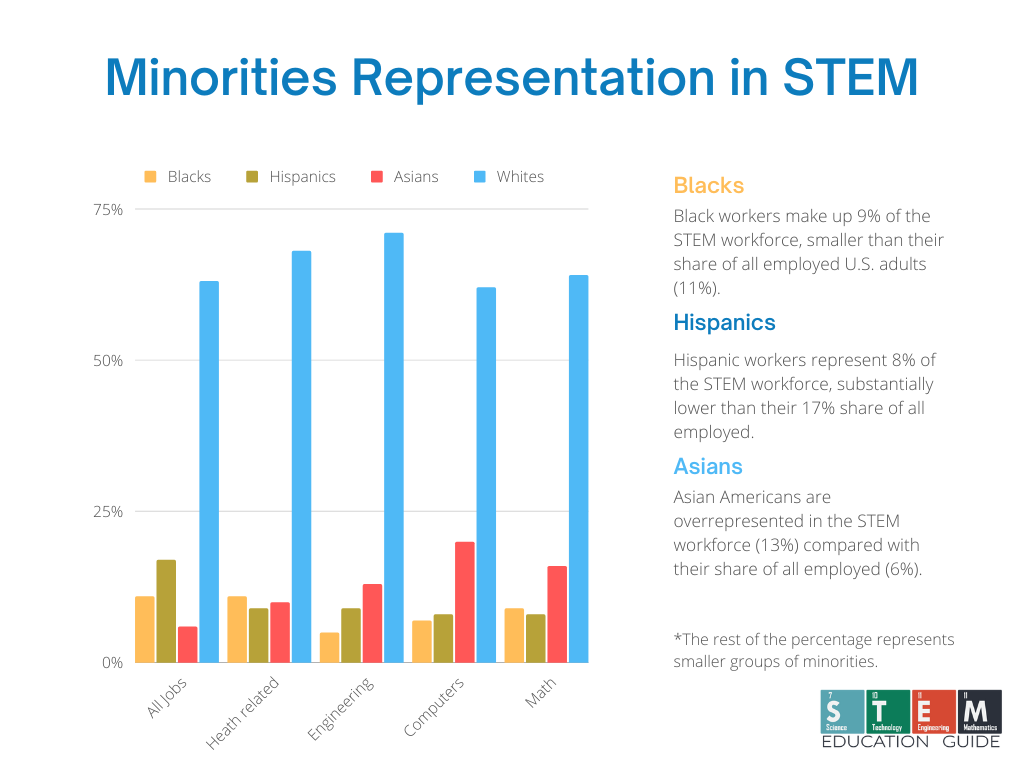
Diversity and Inclusion in STEM
Initiatives: Bold steps are being taken by organizations like the National Science Foundation (NSF) to involve a more diverse population in the sciences.
They recognize the importance of nurturing talent from underrepresented groups such as black and hispanic communities, and have developed initiatives aimed at encouraging their participation in STEM.
The numbers: Surprisingly, only a sliver of NSF funding goes towards such initiatives, but it’s a growing priority.
With schemes like the INCLUDES program, the goal is to dramatically shift the needle on this.
Education: Let’s not forget the folks standing in front of the classroom.
STEM teachers hail from all different backgrounds and are critical in shaping young minds.
The U.S. Department of Education understands this; hence, it pours resources into training a workforce of educators that mirrors the diversity of their students.
It’s about relatability and the light bulb moments that happen when students see themselves in their mentors.
Women and Minorities in STEM
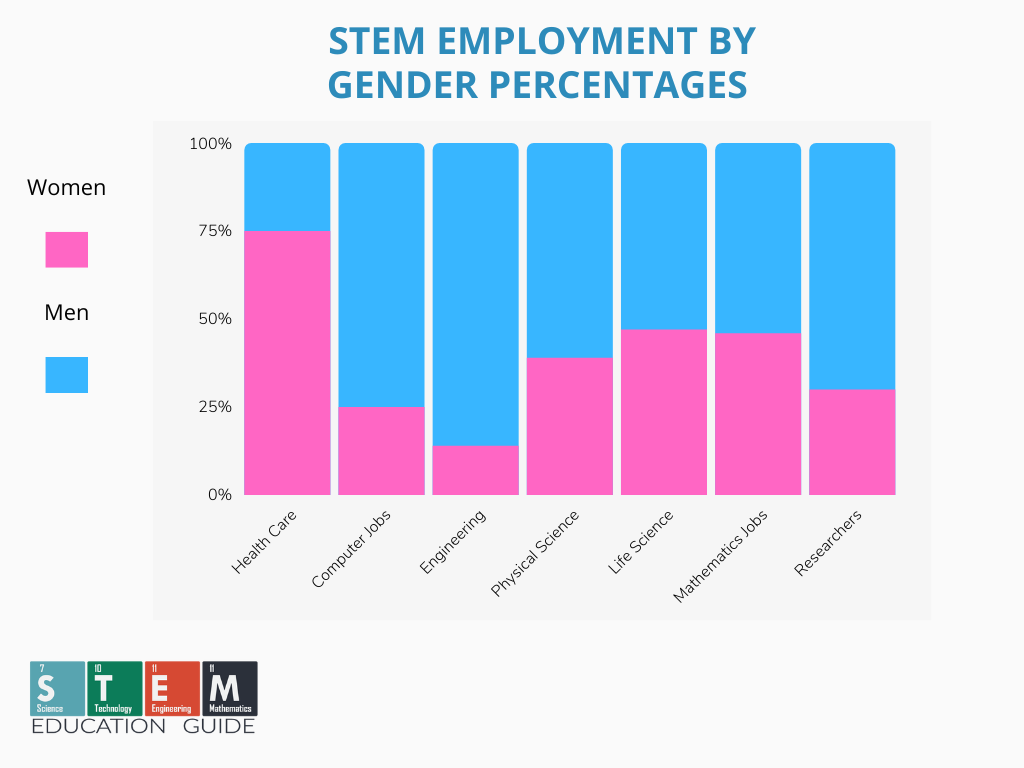
Statistics today: Fasten your seatbelts because the stats are in, and they might rattle you.
Women and minorities are still vastly underrepresented in STEM careers.
Change is on the horizon: But change doesn’t come from just sitting back.
Groups like the Society of Hispanic Professional Engineers (SHPE) and initiatives from the White House aim to rewrite this stale narrative by creating environments where everyone gets a fair shot at success.
Community and Support: It’s all about building a community now, isn’t it?
For women and minorities, this is a game changer.
These initiatives provide both a shoulder to lean on and a springboard to soar from – figuratively speaking. They’re creating a sense of belonging in places where it was scarce – that’s the magic ingredient for a thriving career in STEM.
International Perspective
STEM Around the World
In Australia, students are embracing STEM to become pivotal players in the global economy.
Their education system focuses on innovation and practical applications, pushing students to think beyond the textbook.
On the other hand, China is sprinting forward in STEM.
With a considerable push from the government, Chinese students often outshine others in international rankings like PISA. This shows that they aren’t just good at taking tests — they’re also becoming champions of innovation.
France and the United Kingdom are no slouches either.
They link STEM closely to economics, ensuring their citizens are equipped for future markets. Both nations believe in starting STEM education early, fostering a sense of intrigue and creativity in young minds.
Comparative Education Systems
Let’s get down to the nitty-gritty. How do education systems stack up?
The U.S. government has been a formidable force in promoting STEM, yet there’s room for improvement.
This is especially true when I peek at PISA scores, which show that American students often lag behind their peers in places like East Asia.
Comparing these systems feels like flipping through a kaleidoscope of methodologies.
Some countries stress rote learning, while places like the United Kingdom emphasize a more hands-on approach.
Every country I look at has its way of doing things, but no matter the method, the aim is the same: to equip students with the skills needed for a tech-driven future.
Advancements and Future of STEM
I’m about to walk you through a maze of brainy breakthroughs and a sneak peek at the skills you’ll need to thrive in the fast-moving STEM job market.
Innovations in STEM Education
In my journey through the world of STEM, I’ve seen some real game-changers in education.
We’re not just talking about learning science and math anymore. It’s how these subjects swirl together with technology and engineering that really spices things up.
We’ve moved beyond the classroom walls, with long-distance learning making a serious splash.
And you bet, arts are getting into the mix too—hello, STEAM! This creative buddy brings a whole new layer of imagination and innovation.
- Integration: Subjects are interlocking like pieces of a puzzle, making learning a whole scene and not just scattered bits.
- Creativity: Ditch the yawn-worthy lectures. Educators are crafting courses that light fires under our seats with exciting projects.
- Communication: It’s not a one-way street anymore. Students talk back, brainstorm, and swap ideas like Pokémon cards.
Industry Growth and Future Skills
Move over, old-school careers; the STEM industry’s growth is like popcorn at the movies—fast and massive.
My best guess is a rise in jobs across computer science, health, medicine, and robotics.
But wait, there’s more. We can’t ignore the hefty role of computing across other sectors, like economics, spurring on development and fattening up the economy.
- Future Skills: Jobs are clambering for folks with smarts in:
- Computing: From writing code to cybersecurity—basically anything that makes you feel like a wizard.
- Data Analysis: It’s all the rage, like the avocado on toast of skills.
- Adaptability: Tech’s sprinting, not strolling, and keeping up means lacing up those flexible thinking shoes.
STEM’s trajectory is clear: innovate, integrate, and keep learning fun while polishing up the skills that’ll keep you ahead of the game.
From quantum computing to bionic limbs, the advancements we’re seeing are just the trailer of what’s to come. I’m stoked to see where it all leads—aren’t you?
Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s unravel some common curiosities about STEM education that might be buzzing in your head.
How does STEM education impact high school students?
I’ve noticed high schoolers who get into STEM programs often get a leg-up on critical thinking, problem-solving, and team collaboration.
It’s not just homework; they’re solving real-world puzzles.
What are the key skills developed in STEM programs?
In my experience, STEM hones in on problem-solving and innovation. You learn to tackle challenges with creativity, which is sort of like flexing your brain muscles in new ways.
Can you tell me about the career paths for STEM graduates?
STEM grads often land in diverse fields, from app development to renewable energy. There’s a ton of options, whether you fancy coding or crafting things.
What types of activities are included in STEM for younger kids?
Let me paint you a picture: it’s less about the ‘sit still and listen’ and more ‘let’s build a volcano!’ Kids get their hands dirty with experiments and interactive projects that make learning a blast.









